
Ukraine urgently needs drones, as well as skilled drone operators — military expert Serhiy Zgurets
As the country gears up to produce one million drones this year, the demand for proficient drone operators becomes increasingly critical for the Armed Forces
The need for skilled drone operators is growing
The National Association of Ukrainian Defense Industries, along with unmanned systems manufacturers and training centers for drone operators, has sent an open letter to Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal and Defense Minister Rustem Umerov. The letter highlights a critical need for qualified drone operators as the country aims to produce at least 1 million drones this year, primarily FPV drones, with growth in other drone classes.
However, the Ministry of Digital Transformation and the Ministry of Defense currently don't fund the training of drone operators in private schools due to a lack of regulations. Additionally, there's a shortage of training centers in the Ministry of Defense. The appeal suggests involving the private sector of the defense industry to address this shortage, similar to how it was done to boost domestic drone production.
The letter proposes legislative improvements to address this issue. While there's optimism about future actions, the response from the Ministry of Digital Transformation and the Ministry of Defense is awaited.
Let me remind you that, on average, our teams use around 1,000 FPV drones per month, not including stocks and reserves. When adequately supplied, each operational team can deploy 15 FPV drones for an operation. This is considered effective, with experienced warriors noting that typically, every third target is eliminated with such intensity.
FPV drones are becoming crucial in certain areas, particularly in targeting moving objects or enemy personnel. The development of strike drones is advancing, leading to the emergence of new tactics and practices. Drones enhance the capabilities of our artillery, which, alongside infantry, now plays a pivotal role across the entire front. Conversations with experienced officers highlight the importance of artillery on the battlefield.
Frontline situation: Bakhmut direction
Denys Nahorny, Major of the National Guard and Chief of Staff of the Artillery of the 4th "Rubizh" Brigade, shared updates on the situation in the Bakhmut direction. The offensives are primarily concentrated towards Vesele, Klishchiivka, Andriivka, and Chasiv Yar, with the enemy aiming to reach the edge of the Siverskyi Donets river channel.
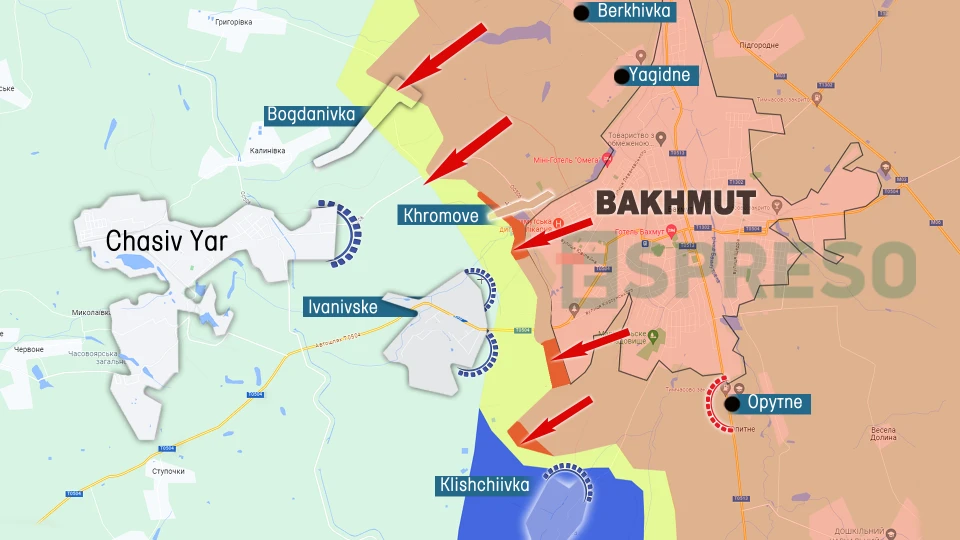
The enemy strategy involves deploying a significant number of infantry, keeping their armored vehicles in reserve and sparingly using them in major assaults. Their objective is to gain an advantage and achieve success. However, the Russians currently lack this advantage due to the destruction of most of their armored vehicles used in offensive operations. In 99% of their offensives, the occupiers face setbacks, as they deploy poorly trained assault groups in front of the front line, essentially using them as cannon fodder. Once the cannon fodder is eliminated, the armored vehicles are then brought into action. Fortunately, our drones detect enemy forces in advance, preventing them from reaching our infantry.
The military serviceman outlined the tactical sequence of actions. Initially, a drone takes off to observe both the front and rear of the enemy. The decision is then made on the most efficient and accurate approach to strike the enemy. It's not about the quantity of tasks; the Armed Forces prioritize quality, as specified in their orders.
The major emphasized that in 60% of cases, mortars are deployed irrespective of weather conditions for tactical success against enemy targets. This is due to the impact of weather on drone usage. Drones, being more precise weapons, are currently insufficient in number, leading to a collection drive for drones. When drone use isn't feasible, a designated amount of ammunition is employed for tactical operations.
Nahorny confirmed the shortage of ammunition for specific offensive and assault operations but assured there's enough for defensive purposes. Statistically, the Armed Forces possess 3 thousand shots compared to the Russians' 10-12 thousand, aided by support from the DPRK. Despite being outnumbered, we strategically target and destroy specific enemy objectives. Our strength lies in counter-battery combat – once identified, we eliminate the threat. The adversary adopts a bulldozer regime, causing devastation in cities like Popasna and Bakhmut, which were not just damaged but completely wiped off the map.
Misinformation is the primary concern among global risks worldwide
Now, let's discuss the battle for meaning and truth, a confrontation with the enemy on the information front that directly impacts events in the trenches and the use of familiar weapons. Currently, leaders from leading countries are gathered in Davos, Switzerland, for the World Economic Forum. Before this meeting, experts from the World Economic Forum presented a report on global risks, identifying the most significant short-term global threats. Notably, for the first time, categories such as misinformation and false information ranked at the top of the list.
Hryhoriy Lyubovets, a key researcher at the Scientific Research Center of the Military Institute, Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, and a board member of the Center for Communication and Content Security, emphasized that the prevalence of disinformation on forums highlights the top-priority issue of Putin's Russia engaging in genocidal aggression against Ukraine and the world. This disinformation surge is a result of a global offensive by Putin's communication and content forces worldwide. Disinformation, once viewed as direct communication between individuals, has now evolved to impact the very foundations of state development, continental affairs, and the future of international institutions. Take, for instance, the UN, which merely outlines problems, underscoring the critical challenge in the transfer, interpretation, and perception of information today. Modern technologies like generative artificial intelligence, propaganda maneuvers, and communication and content security play a pivotal role in shaping this landscape.
Lyubovets further highlighted that the distribution of information across the entire planet has emerged as the foremost challenge. Addressing this goes beyond the realm of information specialists and media professionals, extending to the involvement of top-tier economists on a global scale. This problem has reached a level of global communication and content aggression with a genocidal nature, demanding direct attention.
- News















































