
Skyguard system: advanced defense against airborne threats
In 2024, Ukrainians respond to air raids much more calmly than they did in 2022. People are more accustomed to Russian shelling, know what to do in such situations, and Ukraine's air defense has become much more effective. This improvement is thanks in large part to Ukraine's allies supplying advanced air defense equipment. One key system is the Skyguard, often referred to as the “guardian of the sky"
Content
- What is Skyguard and what is it called?
- What is the Spada air defense system?
- How does the Skyguard system work?
- Aspide missile and its capabilities
- Technical characteristics of Aspide missiles
What is Skyguard and what is it called?
The Skyguard-Sparrow is a short- to medium-range surface-to-air missile system that uses the American AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missile. This air defense system was developed by the Swiss company Oerlikon Contraves AG, and since the late 1970s, work has been carried out based on the Oerlikon GDF computerized anti-aircraft artillery system.
Subsequently, updated versions were created and given different names. Two of them—the Spanish Toledo and the Italian Spada—were provided to Ukraine.
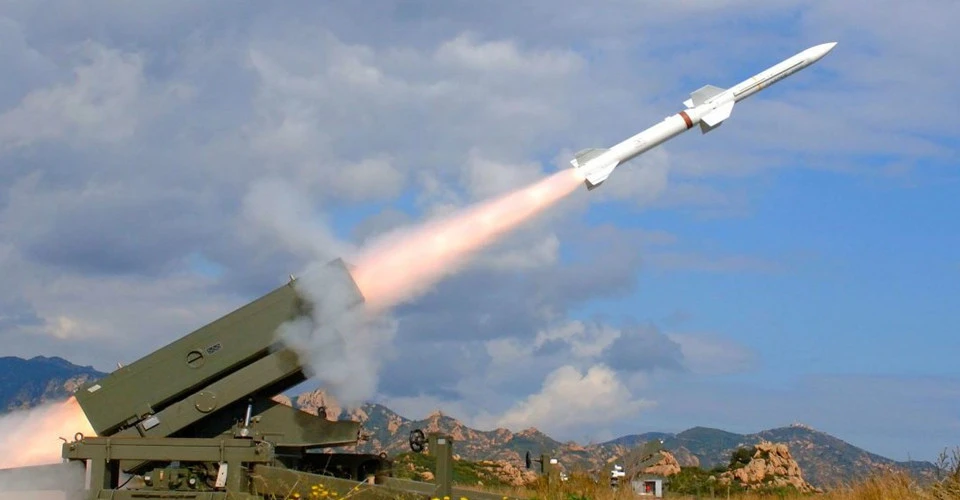

Photo: armyinform
Spain delivered at least one battery of the latest Spada 2000 (4 launchers) in 2022. Official Madrid announced the transfer in the summer. Subsequently, in October and November, the Ukrainian military underwent training at the base in Zaragoza. At the same time, the systems arrived in Ukraine.
In early 2023, Italy also announced the transfer of Spada (Skyguard Aspide) air defense systems. According to La Repubblica, it involved four systems. Each system has three launchers with 6 missiles each. However, no official information on the timing and scope has been made public as Italy does not disclose details regarding military assistance to Ukraine. According to Military Balance, Italy had 32 Spada systems, and Spain had 13 systems.
According to Defense Express observers, Italy is willing to transfer the Spada systems to Ukraine also because it wants to establish exports of these systems. An important factor for this may be the "proven effectiveness in combat conditions" label.
What is the Spada air defense system?
The Spada Aspide (or Skyguard Aspide) system differs from the Skyguard-Sparrow primarily in its missiles: instead of the American AIM-7 Sparrow, the newer Italian Aspide missile is used. The Italian version was developed by Selenia and put into service in 1983. An upgraded version, the Spada 2000, was introduced in 1994.
"The system can be used against airplanes, helicopters, and remotely piloted aircraft, including air-to-ground missiles. All the weapons of the complex are mounted on towed chassis and can be quickly delivered to a given position and, after deployment, be ready for further use," Army Inform says.
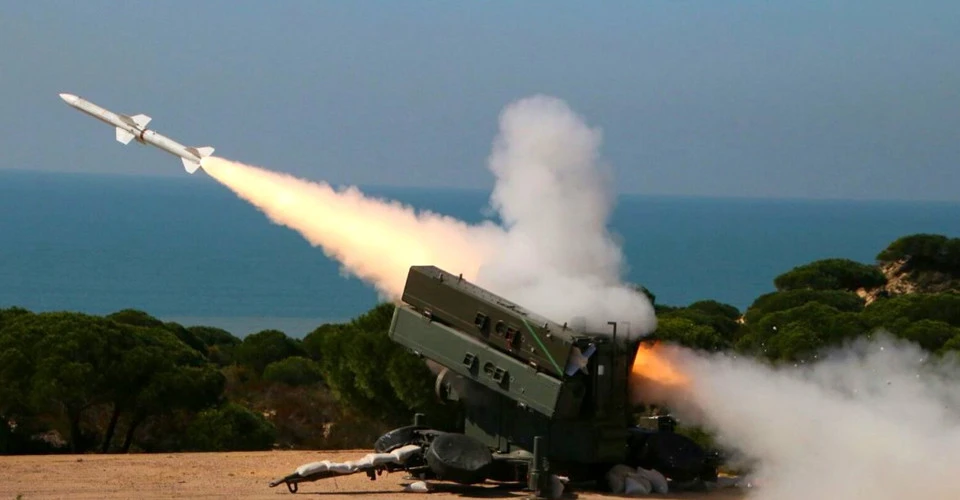

Photo: armyinform
The name Spada translates from Italian as "sword" and is also an abbreviation for "Sistema di Punto Automatizzato per la Difesa Aerea"—"Automated Air Defense System for Object Protection." The main function of the system is to protect strategic objects: airfields, seaports, industrial enterprises, power plants, and grain storage facilities. It intercepts targets flying low, bypassing long- and medium-range systems.
How does the Skyguard system work?
The Aspide Skyguard is a short-range system with semi-active radar guidance. It can destroy targets at a range of up to 10 km with a conventional Aspide missile and up to 20 km with modernized Aspide 2000 missiles. The twin 35-mm cannons fire at a range of up to 4 km with a rate of fire of up to 1,100 rounds per minute.
"Each Spada launcher contains six missiles. The complex includes three launchers, a radar system for detecting and tracking targets, which is part of the Pluto command post, support vehicles, and, optionally, two Oerlikon GDF-001 artillery anti-aircraft systems. Targeting is based on the principle of semi-active guidance; the radar must irradiate the target until it is destroyed, and the missile flies towards the signal reflected from the target," says Defense Express about the system.
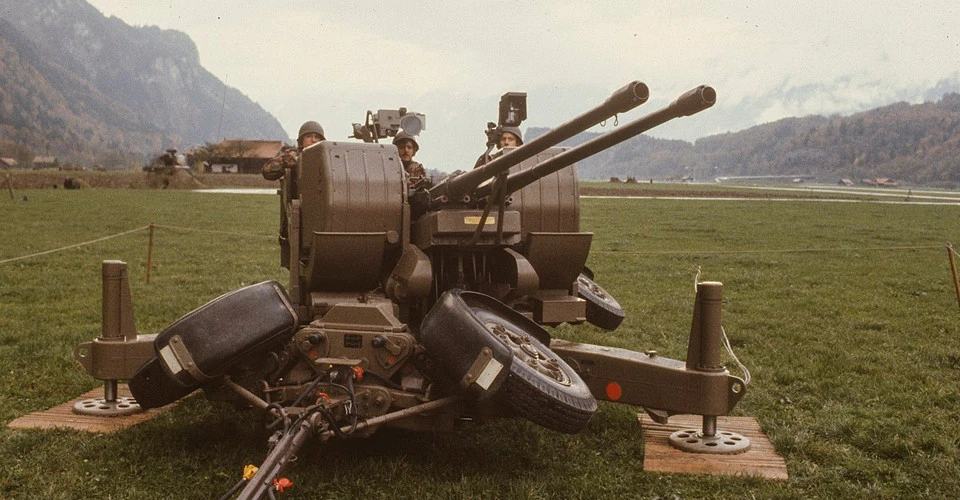
Photo: Wikipedia
Among the advantages of the complex is the ability of the system to work in conjunction with the 35 mm Oerlikon anti-aircraft artillery system or other anti-aircraft artillery systems, which increases the effectiveness of countering air targets at low altitude. Additionally, the Skyguard-Aspide equipment allows it to operate as part of a layered air defense system and exchange data with other types of air defense systems.
Depending on the modification, the surveillance and search radar can monitor the air situation within a radius of up to 20 km. The Skyguard detects targets independently or accepts predefined targets, processes firing data, and controls the launchers. The Aspide launcher is built on a wheeled platform with jacks. The main part of the system with four missile transport and launch containers and two target illumination antennas is placed on the pivoting device.
Aspide missile and its capabilities
The Aspide missile itself is a medium-range anti-aircraft missile developed in the 1980s, a licensed copy of the US AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missile, but with significant changes. The improvements affected all major components of the missile, including engine power, a new homing head, and rudder actuators. Additionally, the dimensions of the missile were increased. The Aspide is more resistant to interference than the Sparrow, has updated electronics, and better maneuverability.
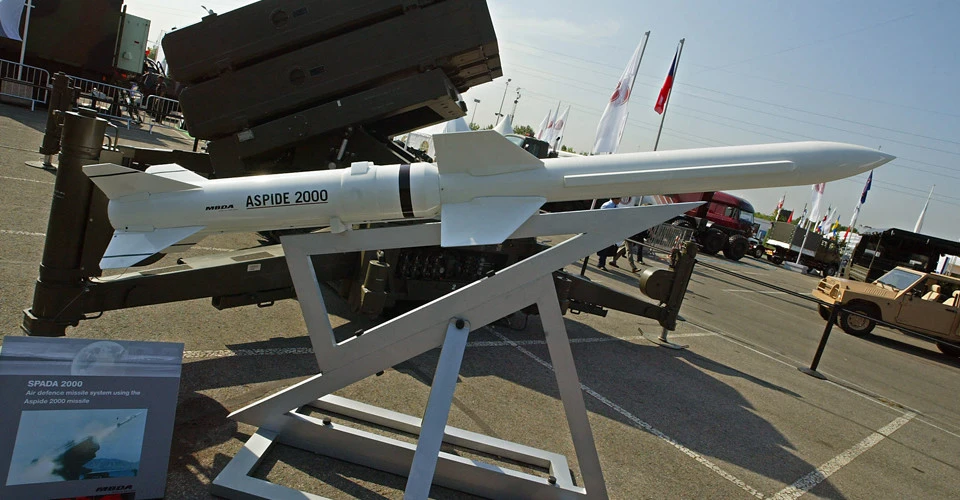

Photo: Getty Images
The missile has semi-active radar guidance. The range is 35 km, and the height of target destruction reaches 6-8 km. The missile accelerates to almost 5,000 km/h. The missile has a launch weight of 228 kg, including a high-explosive warhead of 35 kg.
Technical characteristics of Aspide missiles
- Length: 3.7 m
- Diameter: 0.2 m
- Wingspan: 1 m
- Launch weight: 228 kg
- Warhead: 35 kg
- Maximum speed: 1,324 m/s
- Range: 35 km
- Effective range: up to 25 km
- Ceiling: 8 km.
- News














































